 | |
| Nematode |
Introduction:
Filariasis is, a disease group affecting humans, caused by
nematode parasites of the order Filariidae,
and transmitted by mosquitoes - Culex quinquefasciatus is
globally the most important vector.
3 of the species are primarily responsible for most cases of
human Filariasis
• Wucheraria bancrofti (lymphatic)
• Brugia malayi (lymphatic)
• Onchocerca volvulus (subcutaneous)
 | |
| Loa Lo Parasite |
Sign and Symptoms:
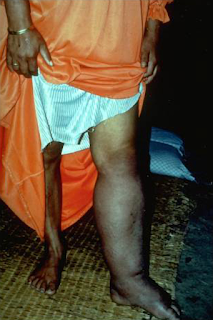 | |
| Filiriasis Patient |
Diagnosis of Filaria:
• Conventional method examination of thick smear
(stained)(counting chamber method)
• Detection of circulating filarial antigen – rapid format
card test/ immunochromatographic card test (ICT)
• Serodiagnosis
• PCR-based assays for DNA
• Imaging studies (high frequency ultrasound,
lymphoscintigraphy)
Note:
Antibody detection provides
an early means to detect filarial parasite infection.
Presence of IgM antibody to
the parasite antigens suggest current infection, whereas, IgG corresponds to
late stage or past infection.
Refrences:
1. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. "Lymphatic Filariasis". Retrieved 18 July 2010.
2. "Lymphatic filariasis". Health Topics A to Z. Source: The World Health Organization. Retrieved 2013-03-24.
3. "Seva Fila" (PDF). JB Tropical Disease Research Centre & Department of Biochemistry, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences.
4. The Carter Center, Lymphatic Filariasis Elimination Program, retrieved 2008-07-17
Jump up ^ U.S. Centers for Disease Control, Lymphatic Filariasis Treatment, retrieved 2008-07-17
5. Bockarie, Moses; Hoerauf, Achim; Taylor, Mark J. (08 October 2010). "Lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis". The Lancet. 376 (9747): 1175-1185. Check date values in: |date= (help);
6. Turkington, Carol A. "Filariasis". The Gale Encyclopedia of Public Health. 1: 351-353.
7. Hewitt, Kirsten; Whitworth, James AG (1 August 2005). "Filariasis". Medicine. 33 (8): 61–64.
8. Gaur RL, Dixit S, Sahoo MK, Khanna M, Singh S, Murthy PK (2007). "Anti-filarial activity of novel formulations of albendazole against experimental brugian filariasis"
Refrences:
1. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. "Lymphatic Filariasis". Retrieved 18 July 2010.
2. "Lymphatic filariasis". Health Topics A to Z. Source: The World Health Organization. Retrieved 2013-03-24.
3. "Seva Fila" (PDF). JB Tropical Disease Research Centre & Department of Biochemistry, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences.
4. The Carter Center, Lymphatic Filariasis Elimination Program, retrieved 2008-07-17
Jump up ^ U.S. Centers for Disease Control, Lymphatic Filariasis Treatment, retrieved 2008-07-17
5. Bockarie, Moses; Hoerauf, Achim; Taylor, Mark J. (08 October 2010). "Lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis". The Lancet. 376 (9747): 1175-1185. Check date values in: |date= (help);
6. Turkington, Carol A. "Filariasis". The Gale Encyclopedia of Public Health. 1: 351-353.
7. Hewitt, Kirsten; Whitworth, James AG (1 August 2005). "Filariasis". Medicine. 33 (8): 61–64.
8. Gaur RL, Dixit S, Sahoo MK, Khanna M, Singh S, Murthy PK (2007). "Anti-filarial activity of novel formulations of albendazole against experimental brugian filariasis"

I really like your Blog. Thanks to Admin for Sharing such useful information. Addition to this here I am Contributing One more Similar Story Lymphatic Filariasis Symptoms, Treatment & Diagnosis.
ReplyDelete